

Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS) is when the arteries supplying blood to the kidneys narrow down. The renal arteries bring oxygen-rich blood to your kidneys, helping them eliminate waste and excess fluid from your body.
RAS-related signs and symptoms include:
Visit your doctor if you experience any unusual symptoms.
Your doctor can start with the following steps to diagnose renal artery stenosis:
Causes of RAS include:
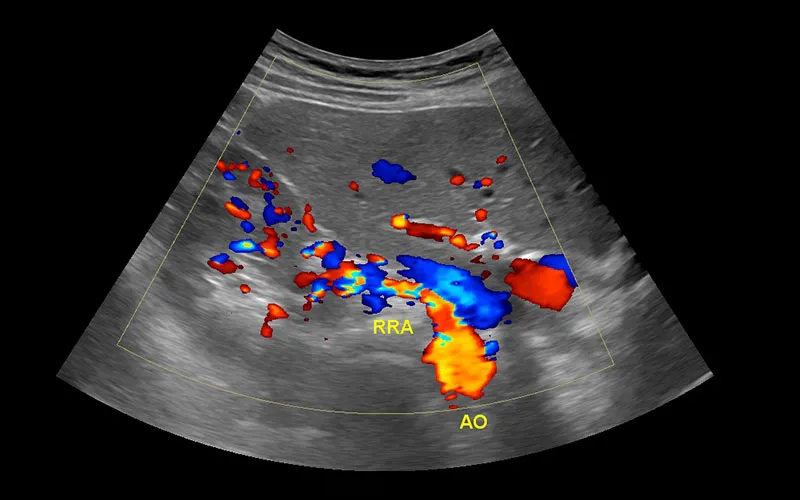
Imaging tests to diagnose renal artery stenosis include:
Treatment for RAS can include lifestyle changes, medication, a procedure to restore blood flow to the kidneys, or a combination of treatments. These treatment methods include:
Your doctor can also prescribe aspirin and a cholesterol-lowering medicine in the case of atherosclerosis.
A procedure to restore blood flow through the renal artery and increase blood flow to the kidney may be prescribed for some individuals.
You may visit your general doctor, or you may be referred to a nephrologist or cardiologist.
If you need an affordable treatment of renal artery stenosis, contact us at North Atlanta Vascular and Vein Center. We provide high-quality treatments for vein diseases.
To prepare for treatment, you can:
Your doctor can ask the following questions: